GPUs have far more processor cores than CPUs, but because each GPU core runs significantly slower than a CPU core and do not have the features needed for modern operating systems, they are not appropriate for performing most of the processing in everyday computing. They are most suited to compute-intensive operations such as video processing and physics simulations.
GPU(Graphics Processing Unit)的core数量比CPU的多,它是显卡(video card)的CPU。由于它的指令集不如CPU强大,但是core数量多,所以适合做一些相对简单的,计算密集性的运算:比如图像处理等等。GPGPU(General Purpose Graphics Processing Unit)则不仅仅只做图像处理的相关运算,也会做一些一般性的运算。
更新:计算机屏幕上的图像是如何显示出来的?这个帖子给了很好的解释:
The GPU has a series of registers that the BIOS maps. These permit the CPU to access the GPU’s memory and instruct the GPU to perform operations. The CPU plugs values into those registers to map some of the GPU’s memory so that the CPU can access it. Then it loads instructions into that memory. It then writes a value to a register that tells the GPU to execute the instructions the CPU loaded into its memory.
The information consists of the software that the GPU needs to run. This software is bundled with the driver and then the driver handles the responsibility split between the CPU and GPU (by running portions of its code on both devices).
The driver then manages a series of “windows” into GPU memory that the CPU can read from and write to. Generally, the access pattern involves the CPU writing instructions or information into mapped GPU memory and then instructing the GPU, through a register, to execute those instruction or process that information. The information includes shader logic, textures, and so on.
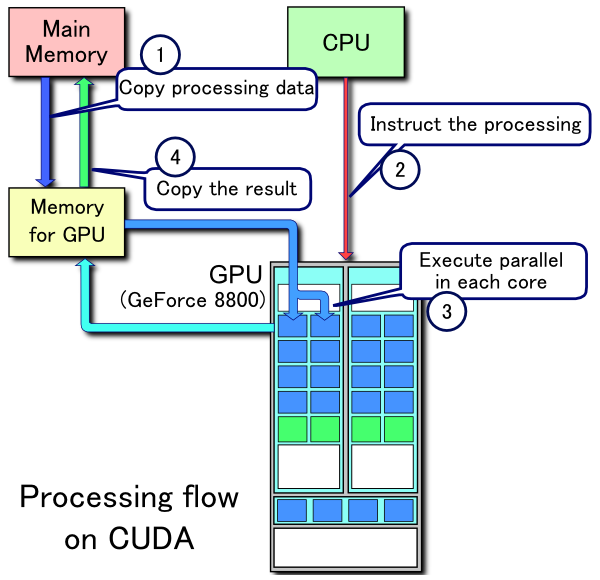
简单地讲,CPU会把要显示的图像和指令存到显卡(video card)的register中,然后通知GPU(显卡上的CPU)去执行画图命令。 此外,wiki百科上的这张图形象地描述了整个过程:
How does the CPU and GPU interact in displaying computer graphics?。