双向链表是Linux kernel中常用的数据结构,定义如下:
struct list_head {
struct list_head *next, *prev;
};
#define LIST_HEAD_INIT(name) { &(name), &(name) }
#define LIST_HEAD(name) \
struct list_head name = LIST_HEAD_INIT(name)
static inline void INIT_LIST_HEAD(struct list_head *list)
{
list->next = list;
list->prev = list;
}
...
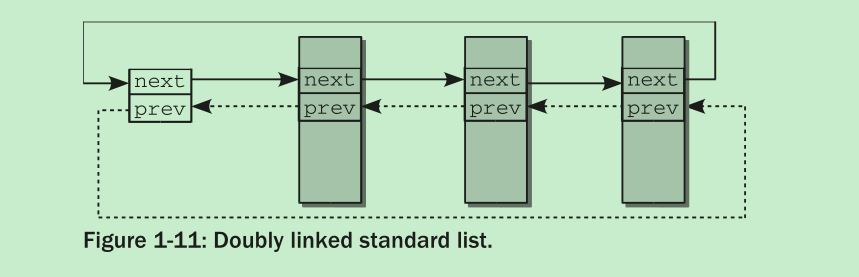
下图选自plka:
从上图可以看出,定义链表需要一个头结点,通过头结点继而可以完成插入,删除元素等操作。来看一个例子(list.c):
struct list_head {
struct list_head *next, *prev;
};
#define LIST_HEAD_INIT(name) { &(name), &(name) }
#define LIST_HEAD(name) \
struct list_head name = LIST_HEAD_INIT(name)
int main(void) {
LIST_HEAD(dev_list);
return 0;
}
检查gcc预处理的输出:
# gcc -E -P list.c
struct list_head {
struct list_head *next, *prev;
};
int main(void) {
struct list_head dev_list = { &(dev_list), &(dev_list) };
return 0;
}
可以看到,头结点dev_list的prev和next都指向了自己。下面代码达到同样的效果:
struct list_head {
struct list_head *next, *prev;
};
static inline void INIT_LIST_HEAD(struct list_head *list)
{
list->next = list;
list->prev = list;
}
int main(void) {
struct list_head dev_list;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev_list);
return 0;
}