对于每一种体系结构,都有一个kernel主配置文件:arch/<arch>/Kconfig。当执行make config/menuconfig/xconfig命令时,如果当前kernel根目录下没有.config文件,则会读取Kconfig文件。
标签: kernel
Linux kernel 笔记 (27)——“make clean”和“make mrproper”的区别
Sometimes, you’ll change things so much that make can’t figure out how to recompile the files correctly. make clean will remove all the object and kernel object files (ending in .o and .ko) and a few other things. make mrproper will do everything make clean does, plus remove your config file, the dependency files, and everything else that make config creates. Be sure to save your config file in another file before running make mrproper. Afterwards, copy the config file back to .config and start over, beginning at make menuconfig. A make mrproper will often fix strange kernel crashes that make no sense and strange compilation errors that make no sense.
make clean删除object和kernel object文件,还有其它一些文件。make mrproper是make clean的超集,它还会删除config文件,依赖文件,以及其它make config生成的文件。
Linux kernel 笔记 (26)——利用“make -j”提高编译`kernel`速度
首先看一下-j选项在make命令中的含义:
-j [jobs], --jobs[=jobs]
Specifies the number of jobs (commands) to run simultaneously. If there is more than one -j
option, the last one is effective. If the -j option is given without an argument, make will not
limit the number of jobs that can run simultaneously.
也就是-j指定并行工作的job数量,例如make -j4。如果-j选项后面没有参数,则不会限制job数。
再参考《Linux kernel development》:
By default, make spawns only a single job because Makefiles all too often have incorrect dependency information.With incorrect dependencies, multiple jobs can step on each other’s toes, resulting in errors in the build process.The kernel’s Makefiles have correct dependency information, so spawning multiple jobs does not result in failures.To build the kernel with multiple make jobs, use
$ make -jn
Here, n is the number of jobs to spawn. Usual practice is to spawn one or two jobs per processor. For example, on a 16-core machine, you might do
$ make -j32 > /dev/null
可以看到指定job数是系统core数量2倍是一种推荐的做法。
Linux kernel 笔记 (25)——什么是vanilla kernel?
kernel.org提供的就是vanilla kernel,而不同的发行版可能会在这个原始的vanilla kernel上做一些改动。例如,改个bug,增加对新设备的支持,等等。
参考资料:
What is vanilla kernel
Linux kernel 笔记 (24)——Kdump是如何工作的
先介绍两个术语:
a)Standard(production)kernel:正常使用的kernel;
b)Crash(capture)kernel:用来收集crash dump的kernel。
Kdump有两个重要的组件:Kdump和Kexec:
a)Kexec:
是一种fastboot mechanism。Kexec允许不通过BIOS,而是从运行的kernel中启动另一个kernel,这样做速度很快,可以节省大量时间。
b)Kdump:
是一种新的,可靠的crash dumping mechanism。Crash dump是从新启动的kernel中去捕获,而不是从已经crashed kernel中。当系统crash后,Kdump使用Kexec启动第二个kernel(Crash kernel),而第一个kernel(Standard kernel)会保留一部分内存供第二个kernel使用。由于Kexec没有通过BIOS启动第二个kernel,因此第一个kernel的内存得到保护,也就是最终的kernel crash dump。
参考资料:
Linux Kernel Crash Book。
Linux kernel 笔记 (23)——安装Suse kernel代码
Linux kernel 笔记 (22)——一个简单的模块Makefile
以LDD3中Compiling and Loading一节的编译模块的Makefile为例:
# If KERNELRELEASE is defined, we've been invoked from the
# kernel build system and can use its language.
ifneq ($(KERNELRELEASE),)
obj-m := hello.o
# Otherwise we were called directly from the command
# line; invoke the kernel build system.
else
KERNELDIR ?= /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build
PWD := $(shell pwd)
default:
$(MAKE) -C $(KERNELDIR) M=$(PWD) modules
endif
当在命令行执行make命令时(当前工作目录即模块源文件所在目录),因为当前模块所在目录里没有定义KERNELRELEASE,所以执行else部分,即把KERNELDIR和PWD变量赋值。
接下来执行“$(MAKE) -C $(KERNELDIR) M=$(PWD) modules”命令。-C选项的含义是把目录切换到KERNELDIR目录下,然后读取KERNELDIR目录下的Makefile。M选项是在编译modules再切换回模块所在目录。此时由于KERNELRELEASE变量已经定义,即可以得知需要编译obj-m。
Linux kernel 笔记 (21)——per-CPU变量
per-CPU变量顾名思义,即当你声明一个per-CPU变量时,当前系统上的每个CPU都会有一份当前变量的copy。使用per-CPU变量好处是访问它几乎不需要加锁,因为每个CPU都有一份copy。此外,CPU可以把这个变量放在自己的cache里,访问起来会特别快。定义per-CPU变量方法如下:
DEFINE_PER_CPU(type, name);
如果per-CPU变量是数组,则定义方式如下:
DEFINE_PER_CPU(type[length], array);
per-CPU变量可以导出,供其它模块使用:
EXPORT_PER_CPU_SYMBOL(per_cpu_var);
EXPORT_PER_CPU_SYMBOL_GPL(per_cpu_var);
要在其它模块使用per-CPU变量,则需要声明:
DECLARE_PER_CPU(type, name);
访问per-CPU变量可以使用get_cpu_var(var)和set_cpu_var(var)这两个macro:
/* <linux/percpu.h>*/
/*
* Must be an lvalue. Since @var must be a simple identifier,
* we force a syntax error here if it isn't.
*/
#define get_cpu_var(var) (*({ \
preempt_disable(); \
&__get_cpu_var(var); }))
/*
* The weird & is necessary because sparse considers (void)(var) to be
* a direct dereference of percpu variable (var).
*/
#define put_cpu_var(var) do { \
(void)&(var); \
preempt_enable(); \
} while (0)
因为kernel线程是允许preemption的,所以在get_cpu_var中需要调用preempt_disable,并且要和put_cpu_var配对使用。
访问另一个CPU的per-CPU变量:
per_cpu(variable, int cpu_id);
Linux kernel 笔记 (20)——设备的major和minor号
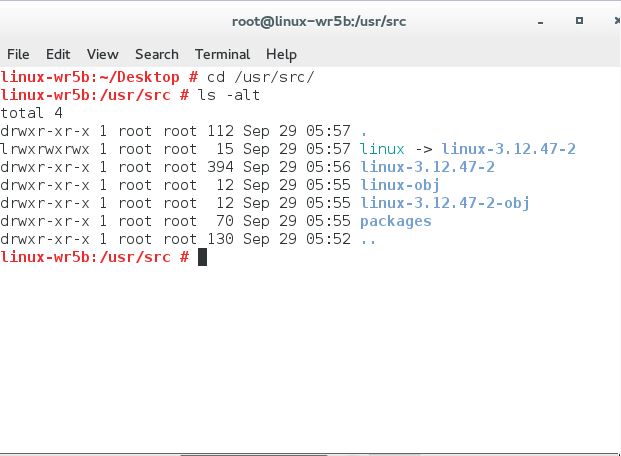
在/dev目录下执行ls -lt命令:
 上面红框框起来的部分就是设备号,前面是
上面红框框起来的部分就是设备号,前面是major,后面是minor。 major号表示设备所使用的驱动,而minor号则表示具体的设备。在上图中,tty的驱动都是driver 4,而利用minor号区别不同的tty设备。 另外,通过/proc/devices文件也可以看到设备所使用的驱动,即major号:
linux-a21w:/dev # cat /proc/devices
Character devices:
1 mem
4 /dev/vc/0
4 tty
4 ttyS
5 /dev/tty
5 /dev/console
5 /dev/ptmx
7 vcs
......关于dev_t,major和minor号定义如下(kernel版本是4.0):
/* <linux/types.h>: */
typedef __u32 __kernel_dev_t;
typedef __kernel_dev_t dev_t;
/* <linux/kdev_t.h> */
#define MINORBITS 20
#define MINORMASK ((1U << MINORBITS) - 1)
#define MAJOR(dev) ((unsigned int) ((dev) >> MINORBITS))
#define MINOR(dev) ((unsigned int) ((dev) & MINORMASK))
#define MKDEV(ma,mi) (((ma) << MINORBITS) | (mi))
dev_t占32 bit长,其中高12位是major,低20位是minor。
获取设备号的两种方法:
(1)预先指定设备号:
int register_chrdev_region(dev_t from, unsigned count, const char *name)
from包含major和minor,通常情况下minor指定为0。count指定连续设备号的数量,name指定设备的名字。register_chrdev_region实现如下:
/**
* register_chrdev_region() - register a range of device numbers
* @from: the first in the desired range of device numbers; must include
* the major number.
* @count: the number of consecutive device numbers required
* @name: the name of the device or driver.
*
* Return value is zero on success, a negative error code on failure.
*/
int register_chrdev_region(dev_t from, unsigned count, const char *name)
{
struct char_device_struct *cd;
dev_t to = from + count;
dev_t n, next;
for (n = from; n < to; n = next) {
next = MKDEV(MAJOR(n)+1, 0);
if (next > to)
next = to;
cd = __register_chrdev_region(MAJOR(n), MINOR(n),
next - n, name);
if (IS_ERR(cd))
goto fail;
}
return 0;
fail:
to = n;
for (n = from; n < to; n = next) {
next = MKDEV(MAJOR(n)+1, 0);
kfree(__unregister_chrdev_region(MAJOR(n), MINOR(n), next - n));
}
return PTR_ERR(cd);
}
可以看到register_chrdev_region即是把from开始连续count个设备号(dev_t类型,包含major和minor)都注册。
举个例子(/drivers/tty/tty_io.c):
register_chrdev_region(MKDEV(TTYAUX_MAJOR, 1), 1, "/dev/console")
(2)动态分配设备号(推荐使用):
int alloc_chrdev_region(dev_t *dev, unsigned int firstminor, unsigned int count, char *name);
dev是传出参数,为动态获得的设备号;firstminor指定第一个minor;count和name同register_chrdev_region的参数定义。alloc_chrdev_region实现如下:
/**
* alloc_chrdev_region() - register a range of char device numbers
* @dev: output parameter for first assigned number
* @baseminor: first of the requested range of minor numbers
* @count: the number of minor numbers required
* @name: the name of the associated device or driver
*
* Allocates a range of char device numbers. The major number will be
* chosen dynamically, and returned (along with the first minor number)
* in @dev. Returns zero or a negative error code.
*/
int alloc_chrdev_region(dev_t *dev, unsigned baseminor, unsigned count,
const char *name)
{
struct char_device_struct *cd;
cd = __register_chrdev_region(0, baseminor, count, name);
if (IS_ERR(cd))
return PTR_ERR(cd);
*dev = MKDEV(cd->major, cd->baseminor);
return 0;
}
举个例子(/drivers/watchdog/watchdog_dev.c):
alloc_chrdev_region(&watchdog_devt, 0, MAX_DOGS, "watchdog");
释放设备号:
void unregister_chrdev_region(dev_t first, unsigned int count);
Linux kernel 笔记 (19)——“soft lockup – CPU# stuck …”bug
“soft lockup - CPU# stuck ...”bug的kernel log类似这样:
[ 28.124107] BUG: soft lockup - CPU#0 stuck for 23s! [init:1]
[ 28.124720] Modules linked in:
[ 28.125247] Supported: Yes
[ 28.125763] Modules linked in:
[ 28.126277] Supported: Yes
[ 28.126774]
[ 28.127264] Pid: 1, comm: init Not tainted 3.0.101-63-xen #1
[ 28.127765] EIP: 0061:[<c00ded0a>] EFLAGS: 00000202 CPU: 0
[ 28.128002] EIP is at handle_mm_fault+0x18a/0x2b0
[ 28.128002] EAX: 0002bfc1 EBX: 00000000 ECX: 00000000 EDX: 00000000
[ 28.128002] ESI: 2bfc1067 EDI: 00000000 EBP: ebfc6200 ESP: ebc35d48
[ 28.128002] DS: 007b ES: 007b FS: 00d8 GS: 0000 SS: e021
[ 28.128002] Process init (pid: 1, ti=ebc08000 task=ebc32ce0 task.ti=ebc34000)
[ 28.128002] Stack:
[ 28.128002] ebfc1778 ebfc6200 00000029 0002bfc1 00000000 080efc90 ebfc2570 ebfc9e40
[ 28.128002] ec7bd000 ebc35dfc 00000003 ebfc2570 080efc90 c0350ad4 00000029 00000100
[ 28.128002] 00000008 00000003 ebfc9e78 ebc32ce0 ebfc9e40 00000000 00000029 00000003
[ 28.128002] Call Trace:
[ 28.128002] [<c0350ad4>] do_page_fault+0x1f4/0x4b0
[ 28.128002] [<c034df54>] error_code+0x30/0x38
[ 28.128002] [<c01da35f>] clear_user+0x2f/0x50
[ 28.128002] [<c01480d4>] load_elf_binary+0xae4/0xc30
[ 28.128002] [<c01094d1>] search_binary_handler+0x1e1/0x2e0
[ 28.128002] [<c01097b4>] do_execve_common+0x1e4/0x280
[ 28.128002] [<c000a9c2>] sys_execve+0x52/0x80
[ 28.128002] [<c035443e>] ptregs_execve+0x12/0x18
[ 28.128002] [<c034dc3d>] syscall_call+0x7/0x7
[ 28.128002] [<c000933f>] kernel_execve+0x1f/0x30
[ 28.128002] [<c000424e>] init_post+0xde/0x130
[ 28.128002] [<c057d638>] kernel_init+0x160/0x18f
[ 28.128002] [<c0354526>] kernel_thread_helper+0x6/0x10
[ 28.128002] Code: 89 f2 89 f8 81 e2 00 f0 ff ff 25 ff 0f 00 00 89 54 24 0c 89 44 24 10 8b 44 24 0c 8b 54 24 10 0f ac d0 0c 89 44 24 0c 8b 44 24 0c <c1> ea 0c 89 54 24 10 c1 e0 05 03 44 24 20 e8 b3 90 ff ff 8b 54
......
这个Bug背后的原理是这样的:
Linux kernel针对每个CPU都有一个watchdog进程。使用ps -ef | grep watctdog可以看到:
[nan@longriver ~]$ ps -ef | grep watchdog
root 6 2 0 Apr20 ? 00:00:16 [watchdog/0]
root 10 2 0 Apr20 ? 00:00:11 [watchdog/1]
root 14 2 0 Apr20 ? 00:00:10 [watchdog/2]
root 18 2 0 Apr20 ? 00:00:09 [watchdog/3]
nan 6726 4608 0 17:28 pts/28 00:00:00 grep watchdog
watchdog进程会搜集所监控的CPU的关于使用时间的信息([watchdog/X]中的X代表监控的CPU ID),并把这些信息存在kernel中。kernel中有专门的interrupt函数会调用softlockup计数器,并把当前的时间与之前kernel中存储的时间值进行比较。如果相差超过一个门限值,则就认为watchdog进程没有获得足够的执行时间用来更新kernel中的信息,也就是CPU一直被其它task占据着。这会被kernel认为是一种不正常的现象,就会打印出如上所示的call trace,register等等信息。