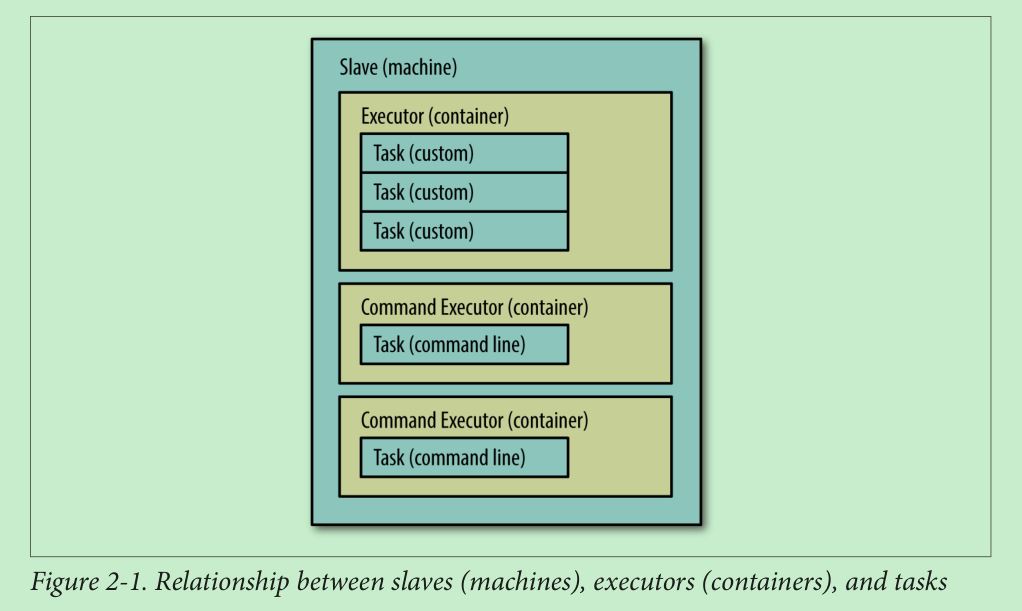
Slave提供资源的例子:

Slave本身属性的定义:

Slave为不同的role预留资源有两种方式:
静态方式:在命令行指定不同的role获得不同的资源:

动态方式:从0.25版本开始,支持通过JSON配置文件和HTTP API方式动态预留资源。
获取资源的函数:
namespace mesos {
namespace internal {
namespace slave {
// TODO(idownes): Move this to the Containerizer interface to complete
// the delegation of containerization, i.e., external containerizers should be
// able to report the resources they can isolate.
Try<Resources> Containerizer::resources(const Flags& flags)
{
Try<Resources> parsed = Resources::parse(
flags.resources.getOrElse(""), flags.default_role);
if (parsed.isError()) {
return Error(parsed.error());
}
Resources resources = parsed.get();
// NOTE: We need to check for the "cpus" string within the flag
// because once Resources are parsed, we cannot distinguish between
// (1) "cpus:0", and
// (2) no cpus specified.
// We only auto-detect cpus in case (2).
// The same logic applies for the other resources!
if (!strings::contains(flags.resources.getOrElse(""), "cpus")) {
// No CPU specified so probe OS or resort to DEFAULT_CPUS.
double cpus;
Try<long> cpus_ = os::cpus();
if (!cpus_.isSome()) {
LOG(WARNING) << "Failed to auto-detect the number of cpus to use: '"
<< cpus_.error()
<< "'; defaulting to " << DEFAULT_CPUS;
cpus = DEFAULT_CPUS;
} else {
cpus = cpus_.get();
}
resources += Resources::parse(
"cpus",
stringify(cpus),
flags.default_role).get();
}
// Memory resource.
......
}
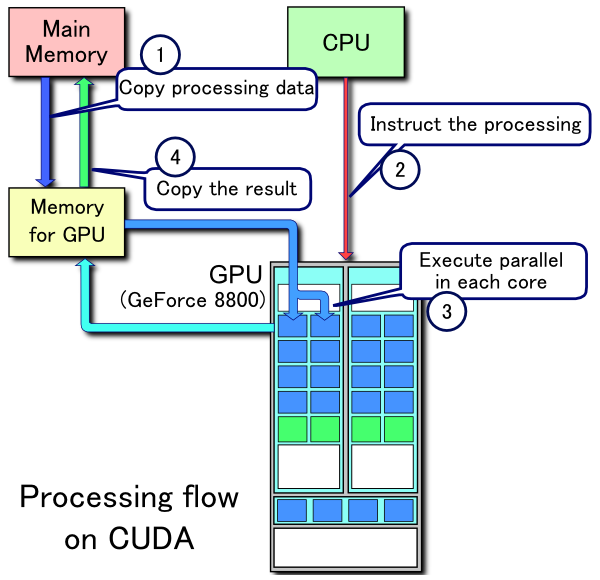
举个例子:启动Slave时参数为--resources=gpgpus:1,则Resources::parse函数会解析gpgpus资源;由于命令行没有提供CPU,memory之类的参数,需要调用os::cpus()等方法来获得。